

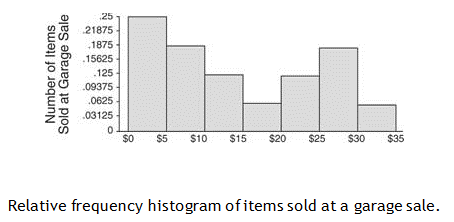
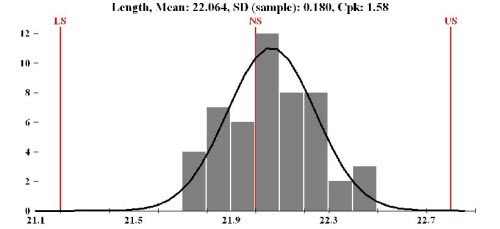
For example: number of children born, categorized against their birth gender: male or female. It shows the number of samples that occur in a category: this is called a frequency distribution. This section aims to show how we can visualize and quantify any variability in a recorded vector of data.Ī histogram is a summary of the variation in a measured variable. The previous section has hopefully convinced you that variation in a process is inevitable. Histograms and probability distributions ¶ Product development and product improvementĢ.4.
Applications of Process Improvement using Data Analysis of designed experiments using PLS models Variability explained with each component A mathematical/statistical interpretation of PLS Advantages of the projection to latent structures (PLS) method Introduction to Projection to Latent Structures (PLS) Visualization latent variable models with linking and brushing Using indicator variables in a latent variable model Determining the number of components to use in the model with cross-validation Algorithms to calculate (build) PCA models Preprocessing the data before building a model Interpreting loadings and scores together More about the direction vectors (loadings) Extended topics related to designed experiments Blocking and confounding for disturbances Highly fractionated designs: beyond half-fractions Generators: to determine confounding due to blocking Generating the complementary half-fraction Example: analysis of systems with 4 factors Assessing significance of main effects and interactions Example: design and analysis of a three-factor experiment Analysis of a factorial design: interaction effects Analysis of a factorial design: main effects Changing one single variable at a time (COST) Experiments with a single variable at two levels Design and analysis of experiments in context Outliers: discrepancy, leverage, and influence of the observations
More than one variable: multiple linear regression (MLR) Summary of steps to build and investigate a linear model

Least squares models with a single x-variable The industrial practice of process monitoring Statistical tables for the normal- and t-distribution The normal distribution and checking for normality General summary: revealing complex data graphically


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
